The SMARTFACTORY project “Research in enabling technologies for smart systems in the factories of the future”, which is financially supported by the Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI), focuses on research into technologies for smart systems that can help us build the factories of the future. The vision of the project is a highly automated and collaborative world, where smart robotics combines its efforts with people’s creativity and adaptability.
SMARTFACTORY aims to make a substantial technological leap forward compared to today’s standard, contributing to every aspect of this vision.
SMARTFACTORY would fall under the umbrella of what is being called Industry 4.0. Behind this concept there are numerous technologies that will provide factories with the ability to adapt continuously and immediately to different tasks, change the products that are manufactured and adapt them to the specific needs of each customer or user. In short, the advantages of a customised solution at the price of mass production.
The SMARTFACTORY project aims to research and advance technologies contributing to the deployment of smart systems for the factories of the future. These systems will increase the flexibility of plants and optimise industrial processes, improving their productivity in a high quality environment.
Production plant internal logistics tend to be rigid and this is one of the areas of improvement that will be pursued in this project. The use of robots for assembly and collaborative work will be the other areas on which this project will focus.
The project completely covers the value chain of technology providers, integrators and end-users.
The SMARTFACTORY project aims to research and advance technologies that contribute to the deployment of smart systems for the factories of the future.
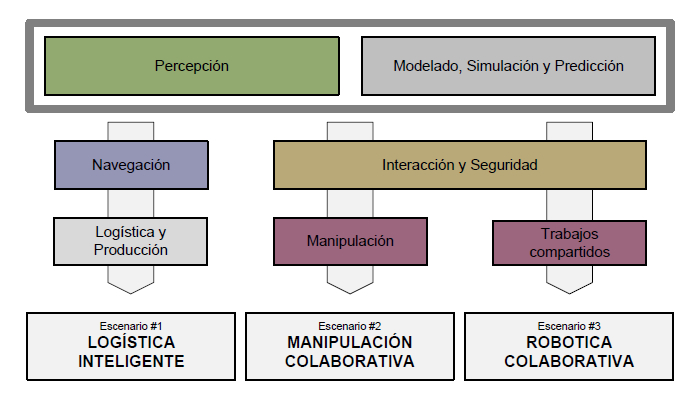
Three industrial application scenarios have been selected to serve as drivers for the technologies to be developed:
- Smart Logistics (Automotive): enabling flexible material and component mobility between storage areas and production lines in unstructured, high-occupancy environments by means of precise, unguided autonomous vehicles without additional infrastructure. There are no pre-defined routes or processes, and traffic adapts automatically.
- Collaborative manipulation (Aeronautics): training robots to handle objects in part assembly applications, without explicit programming. Alternatively, the robot may be shown the task intuitively.
- Collaborative Robotics (Automotive): enabling safe collaborative work between people and robots in confined spaces with shared tasks, adapting robot behaviour to people’s movements and postures.
The project is made up of a consortium of seven companies providing the technology and the three scenarios of use: DGH (leader), LEYTEC (sensors), VIRTUALWARE (virtual simulation), IBERMATICA (ICT, logistics, navigation), FICOMIRRORS (intelligent logistics scenario), CESA (collaborative handling scenario) and CONTINENTAL (collaborative robotics scenario).

Various public and private research organisations are also participating in the project: LEITAT, TECNALIA, IK4-TEKNIKER, EATCO Research Group from the University of Cordoba and the Institute of Robotics and Industrial Informatics, CSIC-UPC.

Funding